- Chembur, Mumbai, 400071
- +91 9136113321 | +91 9930553321
- drsheths@gmail.com | itsdr@hotmail.com
- Mon to Sat: 4pm to 8:30pm
Esophageal metal stenting is a palliative endoscopic procedure used to relieve difficulty in swallowing (dysphagia) caused by advanced esophageal or upper gastrointestinal cancers. It involves placing a self-expanding metal stent (SEMS) in the esophagus to reopen the blocked or narrowed area, allowing patients to eat and drink more comfortably.
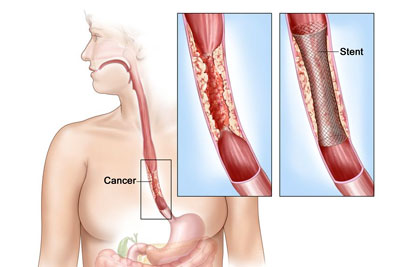
In advanced esophageal cancer or cancers compressing the esophagus from outside, tumors can block the esophagus, making it hard or impossible to swallow. Surgery may not be an option due to disease spread or poor patient health. In such cases, esophageal stenting offers immediate, effective relief.
Yes, it is generally safe and well-tolerated. Some mild discomfort may occur temporarily. Possible but rare complications include:
Esophageal metal stenting is a compassionate, non-surgical approach to restoring swallowing in patients with advanced malignancy, helping them maintain dignity and nutrition in challenging times.